Power Supply Unit
|
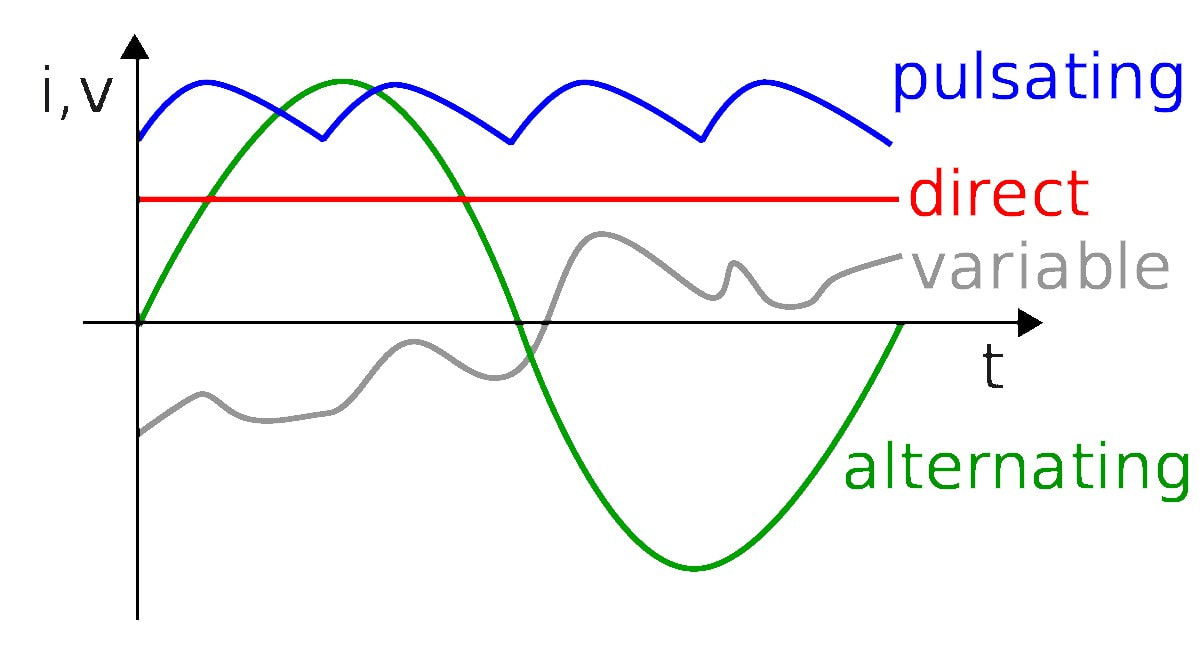
Alternator: an electrical generator that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current (AC) There are two types of current: AC and DC
- electrons move in sine wave caused from alternators -- this wave-like motion means that AC power can travel farther than DC power
- consistent in terms of voltage delivery - rectifier can convert AC to DC AC-DC Power Supply - converts AC power from outlet to unregulated DC
1) Transformer lowers the voltage of AC 2) Rectifier using *diodes converts AC to DC 3) Filter removes "noise" from peaks & troths of the AC power waves 4) Capacitor stores energy from rising edge and expands it when the voltage falls 5) Finally, the current goes through Regulator which reduces ripple voltage, to create a fixed DC output |
*Diode: Allows current to only flow in one direction using a built-in electric field - made up of semi-conductor materials for over-voltage protection
Ex: Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) |
|
Inside Laptop's Internal Battery
- 1Kg of lithium-ion battery can store150 watt-hours of electricity - The notebook connector lets power flow in & out of the battery pack - The tiny motherboard monitors state of battery charged CMOS Battery (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor)
- Usually on the motherboard and powers just the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) - (basic input): CPU sends instruction to hard disk to fetch program - (basic output): Hard disk retrieves data and sends back to CPU - input: CPU runs program sending instructions to GPU - output: GPU sends instruction to monitor to create image Pressing power key (basic input) => Booting up OS (basic output) - Failure Indicator: difficulty booting up, constant beeping noise, date&time reset |
|
Using BIOS to overclock your computer
- All PCs have a set "clock speed" - refers to how fast a computer processor can read incoming electric pulses of information
- Overclocking: when your computer operates at a faster speed than what it was programmed for - may cause your PC to overheat
- All PCs have a set "clock speed" - refers to how fast a computer processor can read incoming electric pulses of information
- Overclocking: when your computer operates at a faster speed than what it was programmed for - may cause your PC to overheat
- How to Overclock:
- - Settings => Update & Security => Recovery => Under 'Advanced Startup' => Restart now
- - Your PC will restart giving you BIOS access - check for an option called: Cell Menu/ AI Tweaker/ CPU settings/ Frequency Controller/ MB Intelligent tweaker
- - Click adjust CPU ratio => Auto settings (hit enter)
- - Choose a number higher than the existing & press return
Hard Drives
|
- Computer's storage: stores OS files, App data, work documents
- It also affects how quickly large files can be transferred There are mainly 2 types of hard drives: SATA and SSD SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment)
- Most commonly used drives for laptops and PCs - Offers about 400 MB/s and uses serial signaling - Evolution: SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) => PATA (Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment) / IDE => SATA |
|
|
SSD (Solid-State Drive)
- Data transfer speed about 550 MB/s - All data is stored on non-volatile flash memory - Pro: fast, more durable | Con: expensive, low disk size
Hybrid drives use magnetic platters (HDD) and flash memory (SSD)
Hard disks and USBs are external memory but there are 2 kinds of internal memory: ROM and RAM
|
|
Internal Memory
ROM (read-only memory)
- non-volatile (stable) memory - It does not lose the stored memory even if it's out of power
- It permanently stores the data that are required to start a PC,
and performs major input/output tasks and holds programs or software instructions
RAM (random access memory)
- volatile (un-stable) memory - temporary storage, memory lost when power is off
- program data first gets loaded into RAM and is then sent to CPU cache
- allows to access multiple programs at once with speed and efficiency
- when opening a new/existing doc, a copy of data for doc is stored in RAM and once saved, gets copied onto HDD/SSD
SRAM (static RAM) - keeps data in memory as long as power is supplied (but expensive so less common)
DRAM (dynamic RAM) - frequently saves data every few millisecond with a new electronic charge
SDRAM (synchronous DRAM) - synchronizes memory speed w/ CPU clock speed ~ 133 MHz
RDRAM (rambus DRAM) - early 2000s video games 1 GHz
DDRSDRAM (double data rate SDRAM) - transfers data on both rising and falling edges of clock cycle
DDR1 - older gen ===> DDR4 - newest gen
- non-volatile (stable) memory - It does not lose the stored memory even if it's out of power
- It permanently stores the data that are required to start a PC,
and performs major input/output tasks and holds programs or software instructions
RAM (random access memory)
- volatile (un-stable) memory - temporary storage, memory lost when power is off
- program data first gets loaded into RAM and is then sent to CPU cache
- allows to access multiple programs at once with speed and efficiency
- when opening a new/existing doc, a copy of data for doc is stored in RAM and once saved, gets copied onto HDD/SSD
SRAM (static RAM) - keeps data in memory as long as power is supplied (but expensive so less common)
DRAM (dynamic RAM) - frequently saves data every few millisecond with a new electronic charge
SDRAM (synchronous DRAM) - synchronizes memory speed w/ CPU clock speed ~ 133 MHz
RDRAM (rambus DRAM) - early 2000s video games 1 GHz
DDRSDRAM (double data rate SDRAM) - transfers data on both rising and falling edges of clock cycle
DDR1 - older gen ===> DDR4 - newest gen
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
CPU is the 'brain' of a computer device - It is a microprocessor made up of a silicon chip containing millions of microscopic transistors
They decide the: speed, efficiency, cache, multi-threading, clock-frequency of computers and mobile devices
They decide the: speed, efficiency, cache, multi-threading, clock-frequency of computers and mobile devices
There are 6 types of CPU cores: Single, Dual, Quad, Hexa, Octa, Deca
- Single core: only one operation can be started at a time
- Dual core: only one operation can be started at a time but the second operation would be started a little
before the first one was over
- So Deca core does not mean 10x faster than the single core
- Faster processors produce more heat due to high clock speed
- To maximize the potential of multi-processors, both OS & program must have a special code called SMT
- Deca cores are usually used for 3D gaming, VFX, modeling - ie: Xenon Silver 4114T
- Server CPUs can have up to 78 cores
Front Side Bus = processing speed which connects with RAM
CPUs also contains levels of cache (ie: L1, L2, L3) which serves as buffer between RAM & stores some data
Manufacturers
- CPUs for PCs: Intel - (ie: Core i3, i5, i7, i9; Celeron, Pentium, Xeon; Atom), AMD - (ie: Ryzen 3, 5, 7; A10, 12; Athlon; EPYC; Opteron)
- Single core: only one operation can be started at a time
- Dual core: only one operation can be started at a time but the second operation would be started a little
before the first one was over
- So Deca core does not mean 10x faster than the single core
- Faster processors produce more heat due to high clock speed
- To maximize the potential of multi-processors, both OS & program must have a special code called SMT
- Deca cores are usually used for 3D gaming, VFX, modeling - ie: Xenon Silver 4114T
- Server CPUs can have up to 78 cores
Front Side Bus = processing speed which connects with RAM
CPUs also contains levels of cache (ie: L1, L2, L3) which serves as buffer between RAM & stores some data
Manufacturers
- CPUs for PCs: Intel - (ie: Core i3, i5, i7, i9; Celeron, Pentium, Xeon; Atom), AMD - (ie: Ryzen 3, 5, 7; A10, 12; Athlon; EPYC; Opteron)
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
|
GPU is a specialized electronic circuit designed to rapidly manipulate and alter memory to accelerate the creation of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display device. They are very efficient at manipulating computer graphics and image processing. Their highly parallel structure makes them more efficient than general-purpose central processing units (CPUs) for algorithms that process large blocks of data in parallel. In a personal computer, a GPU can be present on a video card or embedded on the motherboard.
Some devices also have sound card and network interface card (for Wifi connection). |
|
Motherboard
|
A motherboard is simply a printed circuit board with electrical components attached on it. The motherboard is made up of fiberglass (insulator) sheet with very small copper wires printed on it. These copper wires carry current from point to another since it's a conductor. This current is used by CPU, GPU, RAM and other parts that require electric energy to function.
Electrical Components on Motherboard
Capacitors: store excess current Transistors: allow very specific amount of volt required by a device Resistors: transmits an electric current into voltage and dissipate electric power as heat |
|
|
|
|
|
lllllllllllllllllllll